The aerospace and defense industry continues to be a hotbed of patent innovation. Activity is driven by automation, environmental sustainability, and operational efficiency, and the growing importance of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), drones, and satellites. In the last three years alone, there have been over 237,000 patents filed and granted in the aerospace and defense industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Innovation in defense: active noise reduction propellers. Buy the report here.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilizing and reaching maturity.
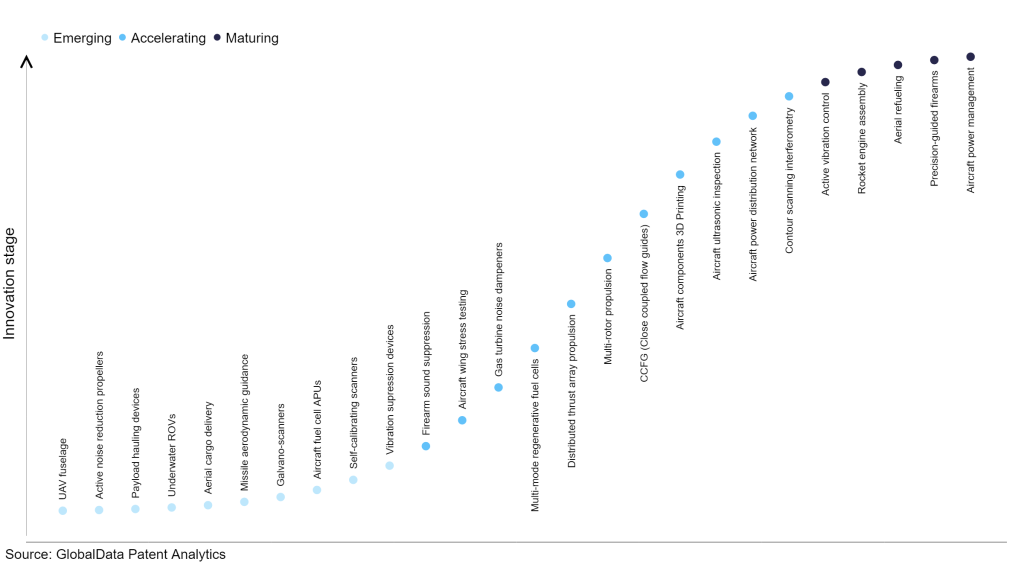
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
110 innovations will shape the aerospace and defense industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the aerospace and defense industry using innovation intensity models built on over 206,000 patents, there are 110 innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, aircraft fuel cell APUs, self-calibrating scanners, and vibration supression devices are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Aircraft ultrasonic inspection, aircraft power distribution network, and contour scanning interferometry are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are precision-guided firearms and aircraft power management, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for the aerospace and defense industry
Active noise reduction propellers is a key innovation area in aerospace and defense
Active noise reduction propellers are devices, systems, and methods used to control, reduce, and/or alter the sound generated by propellers of aerial vehicles, such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), during operation. This can be achieved through various techniques, including adjusting the speed and phase of the rotor units, using acoustic resonators, incorporating sound dampening materials and propeller blade treatments, applying transducers to generate anti-sounds, and actively adjusting the position and/or configuration of propeller blades.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 10 companies, spanning technology vendors, established aerospace and defense companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of active noise reduction propellers.
Key players in active noise reduction propellers – a disruptive innovation in the aerospace and defense industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of applications identified for each patent. It broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of countries each patent is registered in. It reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Patent volumes related to active noise reduction propellers
| Company | Total patents (2021 - 2023) | Premium intelligence on the world's largest companies |
| Dolby Laboratories | 9 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Northrop Grumman | 4 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Panasonic | 15 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Sony Group | 3 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Amazon.com | 67 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Boeing | 5 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Walmart | 1 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Toshiba | 2 | Unlock Company Profile |
| SZ DJI Technology | 13 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Dotterel Technologies | 3 | Unlock Company Profile |
Source: GlobalData Patent Analytics
Boeing is one of the leading patent filers in active noise reduction propellers. The company has filed patent for a special kind of vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) flying vehicle that makes less noise, with multiple rotors connected to the motor being placed in a way that they all point downward in the same direction and some of the rotors having a different shape to create a specific noise pattern.
Boeing, with support from the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), and the US Army, created a special active flap rotor system called smart material actuated rotor technology (SMART), to modify the full-scale five-bladed MD 900 helicopter rotor with piezoelectric-actuated trailing edge flap on each blade of the rotor. The system was developed to substantially reduce the rotor-induced vibration and blade-vortex interaction (BVI) noise.
Other significant patent filers in this space include Northrop Grumman, Dotterel Technologies, and Toshiba that lead both in terms of application diversity and geographic reach.
To further understand the key themes and technologies disrupting the aerospace and defense industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Aerospace & Defense.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.







